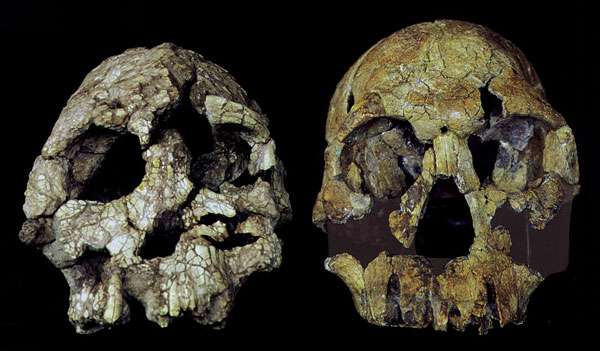
Kenyanthropus platyops
3.5-3.2 million years ago
The discovery in 1998 of a distorted skull, KNM-WT 4000, by a team led by Mauve Leakey in the region west of Lake Turkana in Kenya opened a new controversy in the scientific community. While not yet fully studied, this species, a contemporary of Lucy’s species, A. afarensis, has characteristics, its discoverers claim, that may put it in the direct line to modern humans.
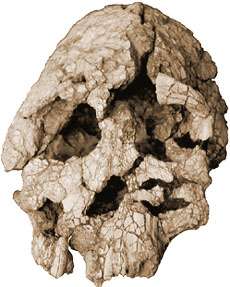
WT 40000 — distorted skull of K. platyops
The species name means “flat-faced” and the new genus name proposed for it means “Man from Kenya” — thus, “flat-faced man from Kenya.” It exhibits a mixture of primitive and modern traits that may revise current views of the development of hominids. For example, if this find is what its discoverers claim it is, then east Africa was home to more than one species of early hominid three million years ago), and the hominid family tree has more branches than anticipated. See Leakey M.G., Spoor F., Brown F., Gathogo P.N., Kiarie C., Leakey L.N. et al. (2001): “New hominin genus from eastern Africa shows diverse middle Pliocene lineages”. Nature, 410:433-40.
Skeptics in the scientific community, however, claim the skull is too distorted to derive any of its morphology with confidence. It is possible, they claim, that the skull belongs to a member of A. afarensis. See White T.D. (2003): "Early hominids - diversity or distortion?" Science, 299:1994-7.
Still others claim that Mauve Leakey is correct in her claims, and this individual seems closer to H. rudolfensis, the earliest known species of the genus homo, than to an australopithecine. See Lieberman D.E. (2001): “Another face in our family tree”. Nature, 410:419-20.